| GF54.00-P-0005-04A | CAN data bus applications | all |  |
| At this time different CAN data bus systems are used for the engine compartment and the passenger compartment. They differ from one another by the rate of transmission.
The CAN engine bus CAN C has a transmission rate of 125 kbit/sec and the CAN passenger bus CAN B has a transmission rate of 83 kbit/sec due to the less critical CAN messages. The data transfer between both data bus systems transpires over so-called "gateways" which are control units that connect both. CAN C/CAN engine compartment On the last control unit on both sides sits the so-called data bus conclusion that has a resistance of 120 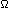 and is switched between both pathways. and is switched between both pathways.
The CAN engine compartment is only active when the ignition is turned on. |
CAN B/CAN passenger compartment
Many of the control units that are found in the CAN passenger compartment are not dependant upon the activation of the ignition (for example, central locking). In this case the CAN passenger compartment has to be accessible with out ignition. This means that it can transmit data telegrams without the ignition being activated. To keep the resting energy consumption as low as possible the CAN data bus goes into a "sleeping mode" if no data telegrams are being transmitted and is activated again when the data bus is accessed. If a "sleeping" CAN passenger compartment control unit sends a CAN message ( for example, the central locking control unit) then the CAN message will only be received by the master (electronic ignition switch, EZS).The EZS saves the the CAN message and sends an activation message (wake-up) to all the control units in the passenger compartment. When waking the control modules, the EZS checks that all stations at available on the CAN data bus and then sends the message previously stored. |