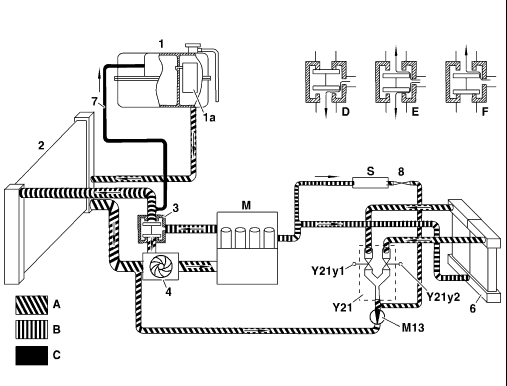
1 Coolant expansion reservoir
1a Silica gel reservoir
2 Radiator
3 Thermostat (position with engine at operating temperature)
4 Coolant pump
6 Heater core
7 Vent line for coolant expansion reservoir
8 Thermovalve
M13 Coolant circulation pump
Y21 Duovalve
Y21y1 Left duovalve
Y21y2 Right due valve
M Engine
S Washing water reservoir, heated by coolant